Shrink Film is an essential material in packaging and protecting various products. Renowned expert Dr. Alice Thompson, a leading figure in the packaging industry, states, "Shrink Film combines flexibility with strength, ensuring goods are preserved during transit." This statement highlights the core qualities of Shrink Film that make it an industry favorite.
The applications of Shrink Film are vast. It is widely used in retail packaging, food preservation, and industrial packaging. The film is usually made from polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride. When heat is applied, the film shrinks tightly around the item. This ensures a secure fit and protection against dust or damage. However, not all Shrink Films are created equal. Some may not adhere properly, leading to potential product spoilage.
In the world of packaging, the effectiveness of Shrink Film often deserves scrutiny. Variability in production can lead to inconsistencies in quality. Some products could be over-wrapped or poorly sealed. These imperfections can hinder the benefits that Shrink Film is meant to provide. Understanding these nuances is crucial for both manufacturers and consumers.
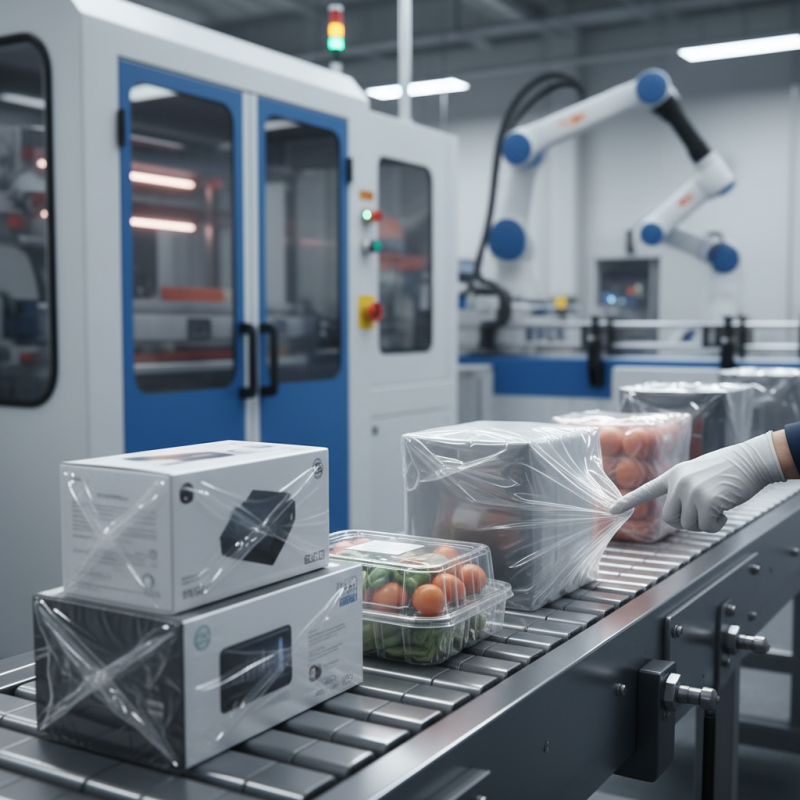

Shrink film is a versatile packaging material widely used in various industries. It is made from plastic. When heat is applied, the film shrinks tightly around products, creating a secure and protective covering. Many manufacturers prefer it for its durability and aesthetic appeal. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global shrink film market was valued at approximately $7 billion in 2021, reflecting a steady growth rate.
In retail and logistics, shrink film is crucial. It helps bundle items together for easy handling, reducing shipping costs and preventing damage during transit. A study by MarketsandMarkets indicates that the demand for shrink film packaging will continue to rise, driven by increased online shopping activities. However, environmental concerns grow as the use of plastics poses significant challenges. Alternatives to traditional shrink film are still being explored, and sustainable practices are needed. Some companies struggle to find greener options while maintaining performance standards.
Users should also reflect on how effective shrink film options are. Not all products require such packaging. Overuse can lead to excess waste, which is counterproductive. Implementing efficient practices will benefit both businesses and the environment. Balancing performance with sustainability remains an ongoing challenge in the use of shrink film.
Shrink film is a versatile packaging material. It is used to wrap items tightly. Various types of shrink film offer different properties. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right one.
Polyolefin shrink film is popular for its clarity. It provides good strength and is resistant to punctures. It works well for food packaging. PVC shrink film is another common option. It has excellent shrinkage properties but can be less durable. Consider the intended use before making a choice.
Tips: Consider the temperature. Different films shrink at different temperatures. Test a small roll first. This can save time and resources. Also, think about thickness. Thinner films may tear easily, while thicker films add durability. Finding the right balance is key.
Shrink film is a versatile packaging solution used across multiple industries. It is a polymer plastic film that shrinks tightly around objects when heated. This unique feature makes it an excellent choice for product protection and presentation.
In the food industry, shrink film is commonly used to wrap perishable items. It keeps products fresh and extends shelf life. Baked goods, such as bread and pastries, are often packaged in shrink film to maintain moisture and avoid contamination. Additionally, retail items like beverages and frozen foods benefit from this packaging method. The film clings tightly to the product, offering a visually appealing finish.
In the industrial sector, shrink film serves various purposes. It is used to bundle products for shipment and secure multiple items together. This improves stability during transportation. Many manufacturers appreciate how shrink film can be printed with labels and branding. However, some users find it challenging to manage waste, as the film can be difficult to recycle. Overall, shrink film plays a crucial role, but considerations around sustainability remain a concern.
Shrink film is a versatile packaging material that transforms through heat. It begins as a flat, flexible sheet. When you apply heat, it shrinks around the item, creating a tight seal. This process protects products from dust and moisture. It can also enhance visual appeal.
The shrinking process involves various techniques. Typically, heat guns or shrink tunnels are used. When the film is heated, the polymer chains tighten. This reaction creates a snug fit around whatever is being wrapped. The result often looks polished. However, not all shrink films perform equally. Factors like temperature and duration can affect the outcome. Sometimes, the seal may not be perfect, requiring adjustments.
Using shrink film can be challenging. It demands precision during application. If the heat is too high, the film can tear. If too low, it may not adhere properly. Observing the process closely is essential. Learning from mistakes helps improve results. Each product may need different settings. Trial and error are regular parts of using shrink film effectively.

Shrink film is a versatile packaging material that offers several benefits. Its primary advantage is creating a tight seal around products. This helps protect them from dust, moisture, and physical damage. Shrink film can easily conform to various shapes and sizes. This adaptability makes it ideal for odd-shaped items. It is commonly used for bundling products or creating tamper-proof packaging. The clear finish also gives a polished look while allowing visibility.
However, there are limitations to consider. Shrink film requires heat to activate. This means additional equipment is necessary. Not all products tolerate high temperatures well, making compatibility an issue. Furthermore, while it provides a robust barrier, it is not biodegradable. This raises concerns about environmental impact. Some users reflect on these factors and seek alternatives. The balance between functionality and sustainability can be challenging.






